M. Chenani
Islamic Azad University, Iran
Title: The effect of SiO2 particle size on hemostatic properties of a novel hybrid as a styptic for severe bleeding
Biography
Biography: M. Chenani
Abstract
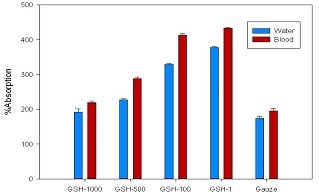
Trauma and its results such as uncontrolled bleeding are some of the most common cause of death. The bleeding and its shock can be cause of serious injuries in vital organs like brain, heart and kidneys in the early stage. Therefore, fast hemostasis is essential as a strategy. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of SiO2 particle size of gelatin/ silica hybrid on hemostatic properties and especially on accelerating the coagulation cascade as a styptic for severe bleeding. The characteristics of blood coagulation (using activated partial thromboplastin time), platelet adhesion (loctate-dehydrogenase), blood and water absorption, structural properties (using UV visible spectroscopy) as well as size analysis (using dynamic light scattering) have been investigated. Hybrid hemostatic behavior varied drastically by changing the particle size, so that the hybrid with micro-meter SiO2 particle size of about 1µm demonstrated very poor ability in platelet adhesion with approximately 3% absorption. Also the activated partial thromboplastin time was just 2 seconds shorter than the normal time, whereas reduction of particle size beyond a certain limit (100nm), led to both increasing platelet adhesion rate to about 28% and very considerable reduction of PTT. In addition, the time of clot formation reduced by 30 seconds in activated partial thromboplastin time test. Alignment of all results showed that particle size reduction improves the hemostatic behavior of the gelatin/ silica hybrid toward its ideal performance by controlling excessive bleeding.
Keywords: particle size; gelatin/silica hybrid; styptic; coagulation cascade.