Janwa El-Maiss
Université de Strasbourg, France
Title: Morphogenic mussel inspired self-construction of versatile enzymatic biosensors by electrochemistry
Biography
Biography: Janwa El-Maiss
Abstract
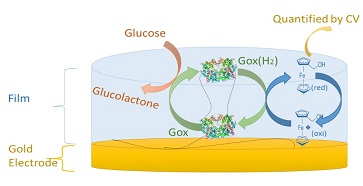
Biosensors have been widely applied due to their high sensitivity, potential selectivity, in addition to the possibility of miniaturization/ automation. Enzyme immobilization is a critical process in biosensors development with the necessity to avoid their denaturation and ensure their accessibility towards the analyte Among all of the enzymes applied in these biosensors, GOx is the most common one owing its importance for detection of blood glucose and its effectiveness in the diagnostic analysis of diabetes.
Electrodeposition of macromolecules is increasingly considered to be the most suitable method for the design of biosensors. Here, we present for the first time the elaboration of a mussel-inspired versatile biosensor using a “One Pot” electrochemical morphogenic approach leading to a covalently cross-linked matrix of biscatechol and glucose oxidase with no leaking observed. The immobilized GOX in the film shows an electrochemical response to glucose using ferrocene methanol as free mediator in solution and has a wide linear range from 1 to 12.5 mM as well as a good sensitivity and affinity to glucose. All these advantageous features allow the development of miniaturized biosensors through functionalization of a single electrode out of a microelectrode array.